3D Pose Detection
Real-time, low-cost pose detection for surveillance and autonomous vehicles
Pose estimation is a computer-based method to detect the position and orientation of a person or object. Researchers at Heriot Watt University have developed a machine learning approach for low-cost cameras to detect human poses.
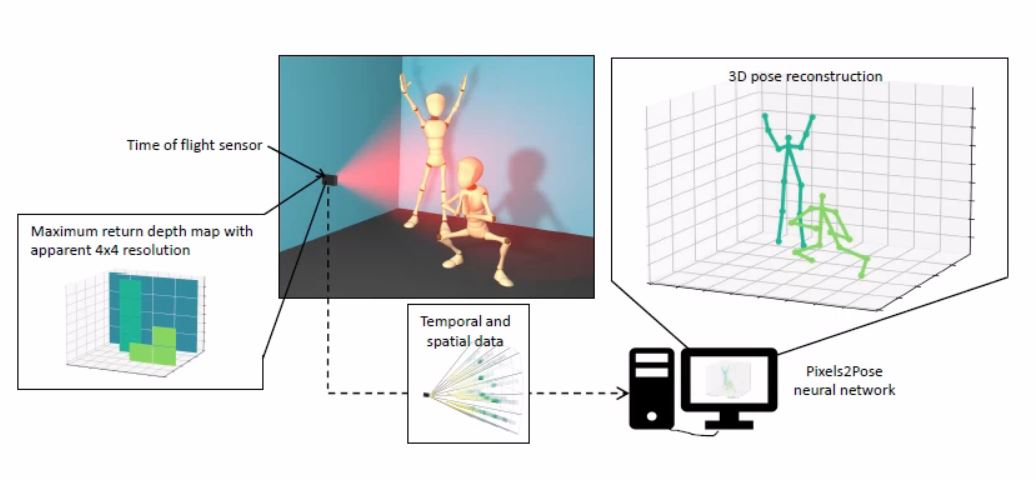
The combined sensor and algorithm can determine 3D positions for multiple individuals using only 16 pixels in real-time.
Traditional 3D pose estimation requires advanced equipment and cameras to produce depth images. The QuantIC 3D Pose Detection sensor uses computational imaging methods to achieve accurate pose estimation, transforming its data into accurate depth maps and 3D pose data of multiple people up to a distance of 3m from the sensor.
Key Benefits
- Low cost compared to traditional methods
- Can generate depth maps at a resolution of 32 x 32 and 3D localisation of body parts
- Use of simplistic sensors allow 3D recognition to integrate into numerous existing devices without additional cost
Applications
- Robot interaction
- Surveillance
- Autonomous vehicles
- Augmented reality and virtual reality

Transport and Defence & Security
Meet our investigator
Dr Jonathan Leach is associate Professor in the School of Engineering & Physical Sciences at Heriot Watt University. His research interests are in developing new classical and quantum optics techniques to solve problems in information science, optical sensing and imaging.
Alice Ruget is part of the Heriot Watt University Quantum Optics & Computational Imaging group and works on computational imaging methods with deep learning to enhance the resolution of SPAD cameras.